Link to Source: Github, Paper, Online Web Application
Summary: Automated AI tool for detecting, classifying, and risk-assessing coronary artery anomalies in CCTA
AAOCA is a fully automated, deep learning-based tool developed for the detection, classification, and anatomical risk assessment of anomalous aortic origin of coronary arteries (AAOCA) in coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) images. This rare but potentially life-threatening cardiac condition can cause ischemia or sudden cardiac death yet is often overlooked or misclassified in routine CCTA examinations. Built on a SEResNet-3D architecture, the system performs three critical tasks: detecting the presence of AAOCA, classifying whether the anomaly originates from the right or left coronary artery, and assessing the anatomical risk level (high or low) to guide clinical decision-making. The tool has been rigorously developed and externally validated on multicenter datasets, demonstrating robust performance across diverse patient populations.
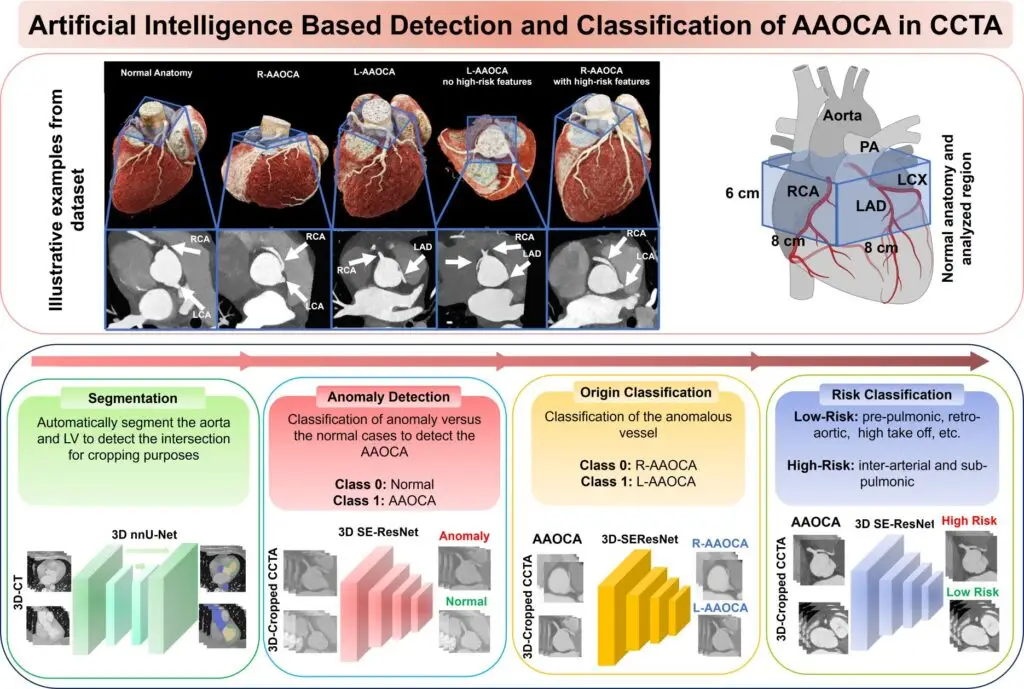
Accessible through both an open-source Python implementation and a user-friendly web application on Medical-Blocks, AAOCA features comprehensive preprocessing pipelines including automated cardiac segmentation, intelligent cropping, and resampling. The system supports ensemble modeling for enhanced prediction accuracy and includes GradCAM++ explainability features that visualize which anatomical regions influenced the AI’s decision, promoting trust and clinical interpretability. Published in Nature Communications (2025), AAOCA achieved excellent detection performance and demonstrated strong generalizability across internal and external validation cohorts. The tool provides fast inference times (under 30 seconds per case with GPU acceleration) and can process both individual cases and batch datasets, making it practical for both clinical workflow integration and research applications in cardiovascular imaging.